Scientific research today takes place across two major environments: wet labs and dry labs. While both play a crucial role in innovation, they differ in tools, processes, and the type of work conducted. Understanding these differences helps research institutions, universities, and industries choose the right lab setup, equipment, and infrastructure.
What is a Wet Lab?
A wet lab is a laboratory environment where scientists work with liquids, chemicals, biological specimens, and experimental materials. This setup involves physical handling of substances that require controlled conditions for safety and accuracy.
Key Characteristics of a Wet Lab
- Involves experiments with chemicals, solutions, and biological samples
- Requires a water supply, proper ventilation, and controlled temperature
- Includes tools like beakers, test tubes, fume hoods, safety cabinets, pipettes, microscopes, etc.
- Essential for fields like biotechnology, microbiology, chemistry, molecular biology, and pharmaceuticals
Common Activities in Wet Labs
- Sample preparation and analysis
- Chemical reactions and testing
- DNA/RNA extraction
- Cell culture and microbiology experiments
Wet labs must follow strict protocols to ensure cleanliness, accuracy, and safety.
What is a Dry Lab?
A dry lab focuses on computational, theoretical, and data-based research. Unlike wet labs, they don’t require chemicals or biological materials. Instead, dry labs rely on software, analytical tools, and digital modeling.
Key Characteristics of a Dry Lab
- Conducts computer-based simulations and analysis
- Requires equipment like computers, servers, and data-processing tools
- Ideal for fields like bioinformatics, computational chemistry, AI modeling, physics simulations, and statistical analysis
Common Activities in Dry Labs
- Data interpretation and research modeling
- Designing experiments before conducting them in a wet lab
- Computational predictions and simulations
- Algorithm development and statistical analysis
Dry labs are essential for optimizing research, reducing experimental errors, and saving time and cost.
Wet Lab vs. Dry Lab: Key Differences
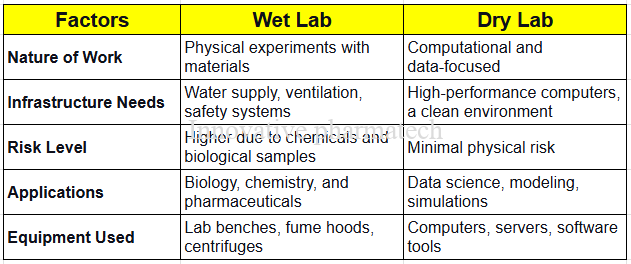
Both types of labs are complementary; data generated in dry labs often supports experiments in wet labs, and vice versa.
Which Lab Setup Do You Need?
Choosing the right lab depends on your research goals:
- For chemical analysis, microbiology, biotechnology: A wet lab is essential.
- For modeling, data analysis, and algorithm development: A dry lab is ideal.
- For interdisciplinary research: A combination of both environments ensures accuracy and efficiency.
Modern research facilities often integrate both labs for streamlined workflows.
Why Quality Lab Infrastructure Matters
- A well-designed lab enhances:
- Safety
- Productivity
- Compliance with industry standards
- Accuracy in research outcomes
Whether planning a wet lab and dry lab, choosing the right lab furniture, airflow systems, and workstations ensures long-term reliability and seamless functioning.
Conclusion
Innovative Pharmatech offers the best solutions for both wet labs and dry labs furniture, highlighting their equally important roles in scientific research. Wet labs focus on hands-on experimentation, while dry labs emphasize computational and analytical work. Together, they form a comprehensive research ecosystem that drives innovation in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, healthcare, engineering, and environmental science.
